IoT: Transforming Industries and Daily Life
 Advanced Health Smartwatch for Women Men with Real-Time Monitoring of Heart rate
Advanced Health Smartwatch for Women Men with Real-Time Monitoring of Heart rate
The Internet of Things (IoT) is revolutionizing the way we live, work, and interact with the world. By connecting everyday objects to the internet, IoT devices enable data collection, automation, and remote control, transforming industries and enhancing human experiences.
Key Principles of IoT
 Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Connectivity
- IoT devices connect to the internet via Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular networks, or other communication protocols.
- This connectivity allows for real-time data transmission and remote control.
Sensing and Data Collection
- IoT devices collect data from various sensors, such as temperature, humidity, motion, and location.
- This data provides insights into the environment, behavior, and usage patterns.
Data Analysis and Processing
- IoT data is analyzed and processed to extract valuable information and patterns.
- This enables predictive analytics, decision-making, and automation.
Actuation and Control
- Some IoT devices can perform physical actions based on data analysis.
- This includes controlling smart home appliances, adjusting lighting levels, or triggering alarms.
Benefits and Applications of IoT
 Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Enhanced Efficiency and Automation
- IoT devices automate tasks, reduce manual labor, and optimize processes.
- For example, smart factories use sensors to monitor production lines and adjust parameters automatically.
Improved Safety and Security
- IoT systems can detect hazards, monitor security cameras, and trigger alerts in case of emergencies.
- This enhances safety in industrial settings, homes, and public spaces.
Personalized Experiences
- IoT devices collect data on user preferences and habits.
- This data is used to provide personalized recommendations, tailored services, and enhanced user experiences.
Environmental Sustainability
- IoT sensors enable real-time monitoring of environmental parameters.
- This data helps organizations optimize energy consumption, reduce waste, and promote sustainable practices.
New Business Models and Opportunities
- IoT opens up new revenue streams for businesses by creating innovative products, services, and data analytics offerings.
- For example, smart cities use IoT to optimize infrastructure and provide personalized citizen services.
Practical Examples of IoT Applications
 ZTE G5 WiFi 7 5G Router, 3600 Mbps Ultra Fast Home & Office Internet, SIM Slot Unlocked, Dual Band, Connect 128 Devices, 2.5 GbE Port, Smart Antenna – Future Ready WiFi 7
ZTE G5 WiFi 7 5G Router, 3600 Mbps Ultra Fast Home & Office Internet, SIM Slot Unlocked, Dual Band, Connect 128 Devices, 2.5 GbE Port, Smart Antenna – Future Ready WiFi 7
Smart Home
- Smart thermostats adjust temperature based on occupancy and preferences.
- Smart lighting systems automate lighting schedules and provide remote control.
- Home security systems use IoT cameras and sensors to detect intruders and send alerts.
Healthcare
- Wearable health devices monitor vital signs, track activity levels, and detect health anomalies.
- Remote patient monitoring systems allow doctors to monitor patients from their homes.
- IoT-enabled medical devices optimize treatment and improve patient outcomes.
Industrial IoT
- Smart factories use IoT sensors to monitor production lines, predict maintenance needs, and optimize processes.
- IoT systems in warehouses enhance inventory management, streamline operations, and reduce costs.
- Predictive maintenance systems use IoT data to identify and prevent equipment failures.
Conclusion
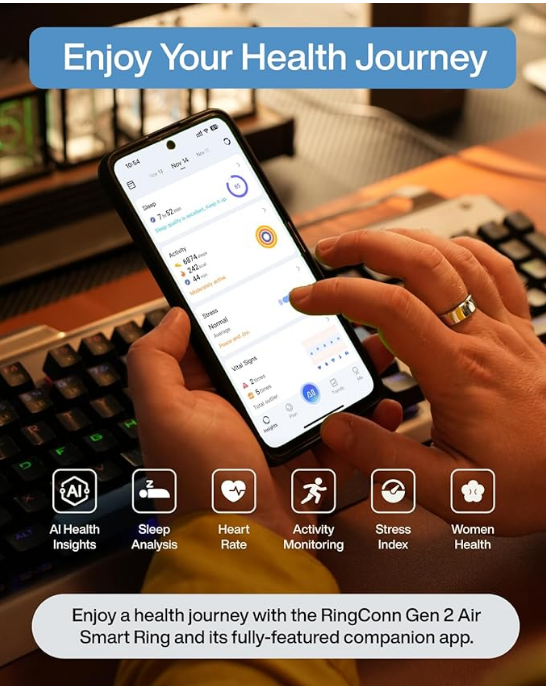 RingConn Gen 2 Air, Ultra-Thin AI Smart Ring, Size First with Sizing Kit, 10-Day Battery Life, Sleep/Heart Rate/Stress/Fitness Tracker, Compatible with Android & iOS - Size 10, Dune Gold
RingConn Gen 2 Air, Ultra-Thin AI Smart Ring, Size First with Sizing Kit, 10-Day Battery Life, Sleep/Heart Rate/Stress/Fitness Tracker, Compatible with Android & iOS - Size 10, Dune Gold
The IoT is transforming industries and daily life at an unprecedented pace. By connecting everyday objects to the internet, IoT enables data-driven insights, automation, and remote control. With its wide-ranging applications, from smart homes to industrial automation, the IoT will continue to revolutionize the way we live, work, and interact with the world. Embracing IoT technologies will empower organizations and individuals to achieve greater efficiency, enhance safety, personalize experiences, promote sustainability, and unlock new business opportunities.

