The Internet of Things: A Comprehensive Guide to the Connected World
 Advanced Health Smartwatch for Women Men with Real-Time Monitoring of Heart rate
Advanced Health Smartwatch for Women Men with Real-Time Monitoring of Heart rate
In an era marked by rapid advancements in technology, the Internet of Things (IoT) has emerged as a transformative force, connecting billions of devices to the internet and revolutionizing industries and daily life. From smart homes to self-driving cars and industrial automation, IoT is shaping the future through unprecedented levels of connectivity and data exchange.
Components of IoT
 Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Connected Devices
The core of IoT lies in the vast array of devices equipped with sensors, actuators, and processors that enable them to communicate with each other and the cloud. Examples include smartphones, smartwatches, smart home appliances, and industrial machinery.
Networks
To exchange data, IoT devices rely on various networks such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, cellular, and low-power wide-area networks (LPWAN). These networks provide connectivity and ensure seamless communication between devices and the cloud.
Cloud Platforms
Cloud platforms play a crucial role in IoT by providing storage, processing, and analytics capabilities for the vast amounts of data generated by connected devices. Major providers like Amazon Web Services (AWS), Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform offer comprehensive IoT solutions.
Benefits of IoT
 Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Increased Efficiency
By automating tasks and optimizing processes, IoT enhances efficiency in diverse industries. For instance, smart sensors in manufacturing can monitor equipment performance, enabling predictive maintenance and preventing costly downtime.
Enhanced Customer Experience
IoT empowers businesses to improve customer experiences. Smart retail applications, such as personalized recommendations and mobile payments, offer convenience and tailored services.
New Revenue Streams
IoT opens up opportunities for new revenue streams. Connected devices generate valuable data that can be monetized through analytics, subscriptions, or personalized advertising.
Improved Decision-Making
IoT provides real-time data and insights that enable businesses to make informed decisions. Smart sensors in healthcare, agriculture, and transportation generate data that can optimize operations and enhance outcomes.
Applications of IoT
 ZTE G5 WiFi 7 5G Router, 3600 Mbps Ultra Fast Home & Office Internet, SIM Slot Unlocked, Dual Band, Connect 128 Devices, 2.5 GbE Port, Smart Antenna – Future Ready WiFi 7
ZTE G5 WiFi 7 5G Router, 3600 Mbps Ultra Fast Home & Office Internet, SIM Slot Unlocked, Dual Band, Connect 128 Devices, 2.5 GbE Port, Smart Antenna – Future Ready WiFi 7
Smart Cities
IoT transforms urban environments with intelligent infrastructure, including traffic management systems, smart lighting, and environmental monitoring.
Healthcare
IoT revolutionizes healthcare by providing remote patient monitoring, wearable devices for health tracking, and AI-powered diagnostics.
Transportation
IoT enables self-driving vehicles, intelligent traffic management, and fleet optimization, enhancing safety and efficiency.
Manufacturing
IoT optimizes manufacturing processes through predictive maintenance, remote monitoring, and robotics, increasing productivity and reducing costs.
Conclusion
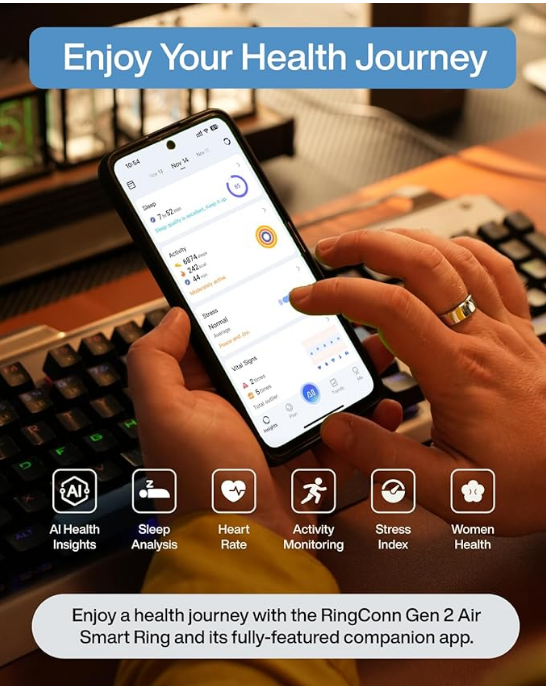 RingConn Gen 2 Air, Ultra-Thin AI Smart Ring, Size First with Sizing Kit, 10-Day Battery Life, Sleep/Heart Rate/Stress/Fitness Tracker, Compatible with Android & iOS - Size 10, Dune Gold
RingConn Gen 2 Air, Ultra-Thin AI Smart Ring, Size First with Sizing Kit, 10-Day Battery Life, Sleep/Heart Rate/Stress/Fitness Tracker, Compatible with Android & iOS - Size 10, Dune Gold
The Internet of Things is a transformative technology that continues to reshape industries and our daily lives. By connecting billions of devices to the internet, IoT unlocks unprecedented levels of connectivity, data exchange, and automation. The benefits of IoT are far-reaching, including increased efficiency, enhanced customer experiences, and improved decision-making. As IoT continues to evolve, it holds the potential to further revolutionize industries, empower individuals, and create a more connected and intelligent world.

