Understanding Semiconductors: The Powerhouse of Modern Electronics
 Advanced Health Smartwatch for Women Men with Real-Time Monitoring of Heart rate
Advanced Health Smartwatch for Women Men with Real-Time Monitoring of Heart rate
Semiconductors, materials with electrical conductivity that falls between conductors and insulators, play a pivotal role in shaping our technological landscape. These remarkable materials are the foundation of modern electronics, enabling breakthroughs in various fields. Let’s delve into their fascinating world to understand their properties, applications, and impact.
Properties of Semiconductors
 Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Intrinsic Semiconductors
- Pure semiconductors, such as silicon and germanium, have a bandgap between the valence and conduction bands.
- At room temperature, only a few electrons have enough energy to overcome the bandgap and become mobile charge carriers (free electrons).
Extrinsic Semiconductors
- When impurities are added to semiconductors, they create additional charge carriers.
- n-type semiconductors have excess electrons due to donor impurities, while p-type semiconductors have excess holes due to acceptor impurities.
Applications of Semiconductors
 Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Lenovo IdeaPad Slim 5 | 14 inch WUXGA Laptop | Intel Core i7-13620H | 24 GB RAM | 1 TB SSD | Windows 11 Home | Cosmic Blue
Diodes
- Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction.
- They are used in rectifiers, voltage regulators, and electronic protection circuits.
Transistors
- Transistors amplify or switch electronic signals.
- They are the building blocks of digital logic circuits, microprocessors, and integrated circuits.
Optoelectronics
- Semiconductors can emit or detect light.
- Light-emitting diodes (LEDs), laser diodes, and photodiodes are used in displays, lighting, and optical communication.
Solar Cells
- Semiconductors absorb photons and convert them into electrical energy.
- Solar cells generate electricity from sunlight and are a key technology in renewable energy.
Benefits of Semiconductors
 ZTE G5 WiFi 7 5G Router, 3600 Mbps Ultra Fast Home & Office Internet, SIM Slot Unlocked, Dual Band, Connect 128 Devices, 2.5 GbE Port, Smart Antenna – Future Ready WiFi 7
ZTE G5 WiFi 7 5G Router, 3600 Mbps Ultra Fast Home & Office Internet, SIM Slot Unlocked, Dual Band, Connect 128 Devices, 2.5 GbE Port, Smart Antenna – Future Ready WiFi 7
- Compact and Lightweight: Semiconductors enable smaller and lighter electronic devices compared to vacuum tubes.
- Energy Efficiency: Semiconductors require less power to operate than vacuum tubes.
- High Performance: Semiconductors can handle high voltage and corriente, allowing for faster and more powerful electronic devices.
- Scalability: Semiconductors can be fabricated in very small sizes, leading to increased circuit density and miniaturization.
- Reliability: Semiconductors are robust and can operate under various environmental conditions.
Impact of Semiconductors
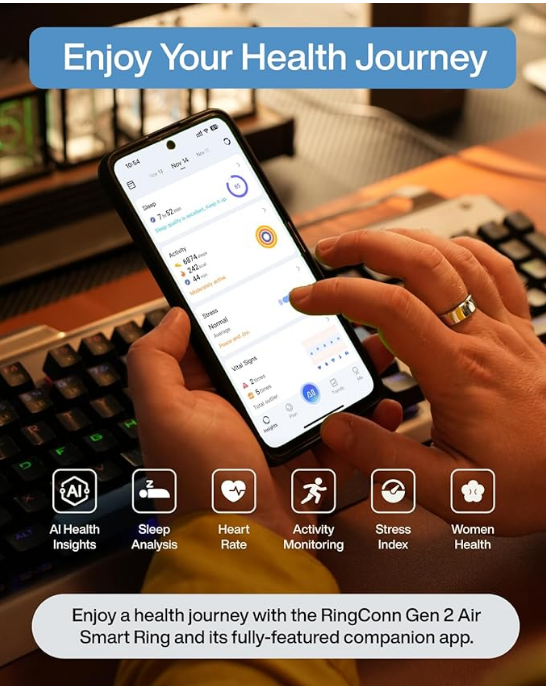 RingConn Gen 2 Air, Ultra-Thin AI Smart Ring, Size First with Sizing Kit, 10-Day Battery Life, Sleep/Heart Rate/Stress/Fitness Tracker, Compatible with Android & iOS - Size 10, Dune Gold
RingConn Gen 2 Air, Ultra-Thin AI Smart Ring, Size First with Sizing Kit, 10-Day Battery Life, Sleep/Heart Rate/Stress/Fitness Tracker, Compatible with Android & iOS - Size 10, Dune Gold
- Revolutionized the electronics industry, enabling the creation of miniaturized and powerful electronic devices.
- Facilitated the development of personal computers, mobile phones, and countless other technologies.
- Contributed to advancements in medical imaging, telecommunications, and renewable energy.
- Expected to continue to play a crucial role in emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, 5G networks, and the Internet of Things.
Conclusion
Semiconductors are indispensable materials that have transformed the electronics industry and enabled countless technological advancements. Their unique electrical properties, coupled with their versatility and ease of fabrication, make them essential components in various applications. As technology continues to evolve, semiconductors will remain at the forefront of innovation, driving the development of the next generation of electronic devices and shaping the future of our digital world.

